TM 5-4310-362-14
4-5.
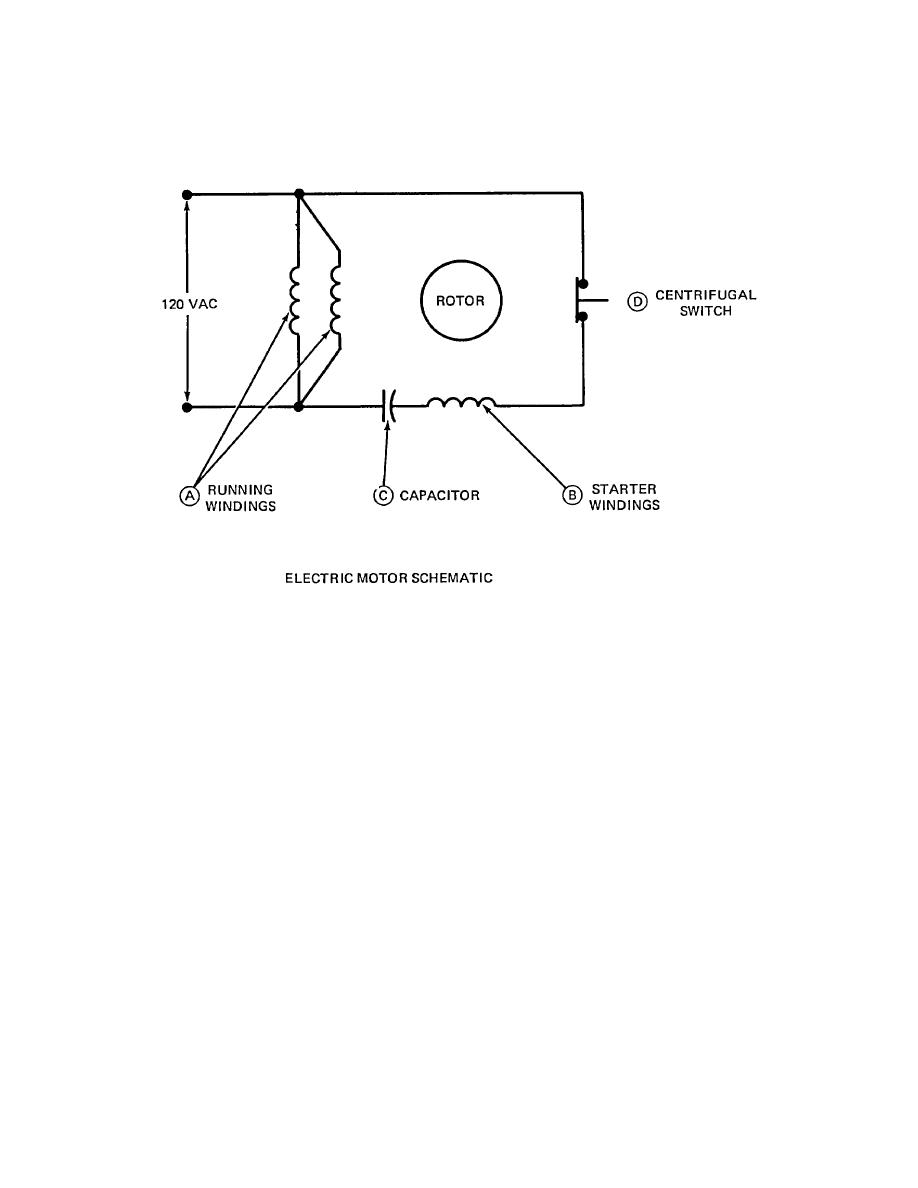
ELECTRIC MOTOR
The electric motor is a single phase capacitor start induction motor.
The running and starter windings A and B make up the stator or stationary windings of the motor. The rotor also contains
a set of windings which have no external connections.
120 VAC comes into the running windings which make up the stator or stationary part of the motor. The alternating
current in the running windings sets up a magnetic field. This field induces a current in the rotor which sets up a magnetic
field opposite to the field in the running windings.
The two opposite fields attract each other and the rotor does not turn except if it is given an initial push. This initial push
comes from the starter windings B and the capacitor C.
The capacitor C causes the current in the starter winding to lead the applied voltage. The shift in phase tarts the rotor
spinning.
Once the rotor is getting close to full speed, the centrifugal switch D opens up. This stops the current through the starter
windings which are made of finer wire and can't sand up to continuous operation.
4-5/(4-6 blank)


